Spring Bean Lifecycle with Executable Code
Lifecycle code example
@Component
public class LifeCycleDemoBean implements
InitializingBean,
DisposableBean,
BeanNameAware,
BeanFactoryAware,
ApplicationContextAware {
public LifeCycleDemoBean() {
System.out.println("## 1. I'm in the LifeCycleBean Constructor");
}
/**
* {@link BeanNameAware}
*/
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("## 2. My Bean Name is: " + name);
}
/**
* {@link BeanFactoryAware}
*/
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("## 3. Bean Factory has been set");
}
/**
* {@link ApplicationContextAware}
*/
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("## 4. Application context has been set");
}
/**
* {@link LifeCycleDemoBeanPostProcessor}
*/
public void beforeInit(){
System.out.println("## 5. Before Init - Called by BeanPostProcessor: LifeCycleDemoBeanPostProcessor");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct(){
System.out.println("## 6. The Post Construct annotated method has been called");
}
/**
* {@link InitializingBean}
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("## 7. The LifeCycleBean has its properties set!");
}
/**
* {@link LifeCycleDemoBeanPostProcessor}
*/
public void afterInit(){
System.out.println("## 8. After init: called by BeanPostProcessor: LifeCycleDemoBeanPostProcessor");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
System.out.println("## 9. The PreDestroy annotated method has been called");
}
/**
* {@link DisposableBean}
*/
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("## 10. The Lifecycle bean has been terminated");
}
}
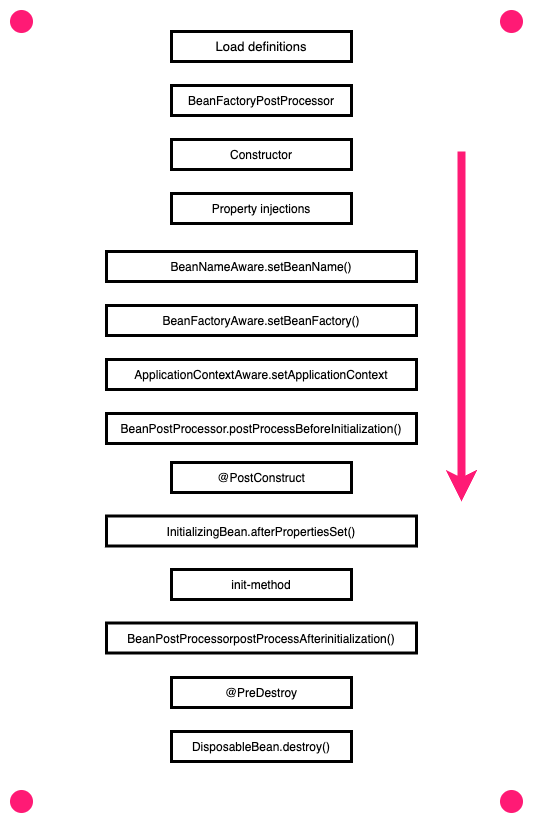
Run the application and then stop it, the printed messages would show in console in the order as their number marks, which is exactly the same as lifecycle image shows:
// run the application
## 1. I'm in the LifeCycleBean Constructor
## 2. My Bean Name is: lifeCycleDemoBean
## 3. Bean Factory has been set
## 4. Application context has been set
## 5. Before Init - Called by BeanPostProcessor: LifeCycleDemoBeanPostProcessor
## 6. The Post Construct annotated method has been called
## 7. The LifeCycleBean has its properties set!
## 8. After init: called by BeanPostProcessor: LifeCycleDemoBeanPostProcessor
// stop the application
## 9. The PreDestroy annotated method has been called
## 10. The Lifecycle bean has been terminated
BeanPostProcessor:
Note that in the above example, the method beforeInit and afterInit are achieved by implement BeanPostProcessor. BeanPostProcessor give us hooks into the Spring bean lifecycle to modify its configuration.
@Component
public class LifeCycleDemoBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(bean instanceof LifeCycleDemoBean){
((LifeCycleDemoBean) bean).beforeInit();
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(bean instanceof LifeCycleDemoBean){
((LifeCycleDemoBean) bean).afterInit();
}
return bean;
}
}